Startup
[ad_1]
Rural startups in India are emerging ventures that address local needs and opportunities in agricultural technology, rural healthcare, and sustainable practices. These startups leverage innovative solutions to bridge infrastructural gaps, empower local communities, and contribute to economic growth in rural areas. They often focus on scalable and inclusive models that harness India’s diverse rural landscape for sustainable development.
In recent times, there has been a surge in rural startups catering to rural needs. The rural startups range from agritech and e-commerce platforms to healthcare and education services which are specifically tailored for rural communities. There has been an unprecedented growth in rural startups with a big government push since 2014.
In India, rural startups encompass diverse models:
- Urban-based Founders Targeting Rural Needs: These startups, led by entrepreneurs from urban areas, leverage technology and resources to address rural challenges. Examples include online platforms linking farmers to markets, telemedicine services, and digital education solutions for rural students.
- Rural-based Founders Serving Local Needs: Entrepreneurs originating from rural backgrounds understand local dynamics intimately, creating solutions like agricultural innovations, rural craft preservation, and community-centric ventures tailored to rural requirements.
- Self-Help Groups (SHGs): SHGs exemplify grassroots entrepreneurship, where community members pool resources to form ventures. Notable examples like Anand Milk Union Ltd. (AMUL) demonstrate successful models of collective enterprise.
- Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in Rural Areas: India’s vast MSME sector, with over 50% situated rurally, spans manufacturing, services, and trade. These enterprises drive economic growth, offering diverse products and services within rural communities.
Examples of Rural Startups in India
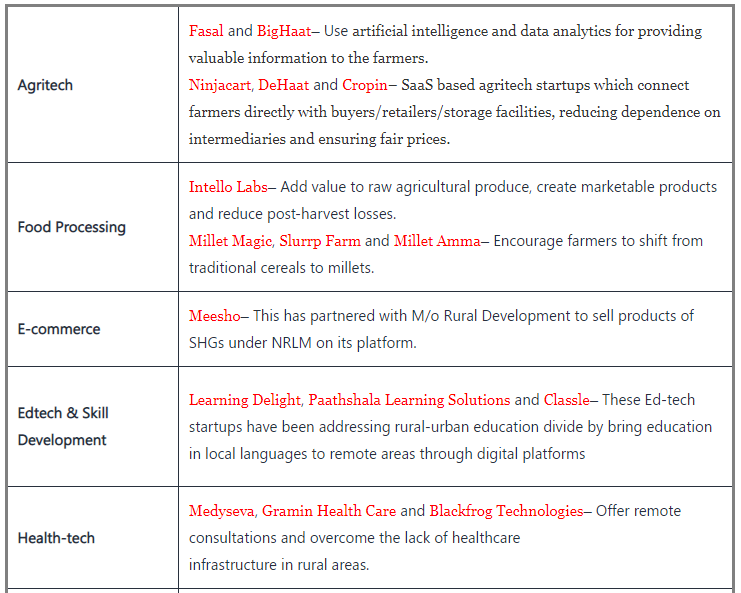

The significance of rural startups in India extends across various critical areas:
- Employment Generation: These startups play a pivotal role in generating employment opportunities for rural youth, addressing the issue of disguised unemployment prevalent in the agricultural sector. This shift is vital for improving overall productivity, considering agriculture’s disproportionate employment-to-GDP ratio.
- Education and Skill Development: Rural startups, particularly in the education technology (ed-tech) sector like Paathshaala, bridge the rural-urban education divide by providing accessible learning platforms. This contributes to skill development and empowers rural communities with knowledge.
- Promotion of Financial Inclusion: Rural fintech startups such as Bank Saathi and Bharatpe are transforming financial services in underserved areas, facilitating digital payment solutions. This fosters financial inclusion, which is crucial for rural development and economic growth.
- Women Empowerment: Startups led by Self-Help Groups (SHGs) like Lijjat Papad and AMUL have significantly empowered rural women, enabling their socio-economic advancement. These initiatives enhance women’s participation in economic activities and decision-making processes.
- Environmental Sustainability: Many rural startups focus on environmental sustainability by harnessing renewable energy sources like biogas, solar, and wind energy. This contributes to India’s vision of a clean and green future while addressing rural energy needs sustainably.
Rural startups in India encounter several challenges that hinder their growth and sustainability:
- Connectivity Gap with Urban Suppliers: Limited connectivity and infrastructure gaps between rural startups and urban suppliers lead to logistical complexities, delays, and increased operational costs, impacting overall efficiency.
- Financial Accessibility: Access to finance is a significant challenge for rural startups due to reluctance from financial institutions to lend to rural enterprises and limited availability of banking services in rural areas.
- Lack of Support System: The absence of robust support systems including mentorship, networking opportunities, and incubation centers in rural areas impedes the growth and development of rural startups, leaving them isolated from essential resources.
- Difficulty in Finding Early Adopters: Rural startups struggle to find early adopters within rural communities due to limited communication channels, lower income levels, and lower digital penetration, which makes market validation and scaling challenging.
- Limited Funding Mechanisms: The majority of startup funding in India is concentrated in urban hubs like Bangalore, Delhi, and Mumbai, with rural startups often overlooked by venture capitalists and angel investors. This lack of funding mechanisms in rural areas restricts the growth potential of rural startups and limits their access to essential resources for scaling and expansion.
What are the Government schemes?
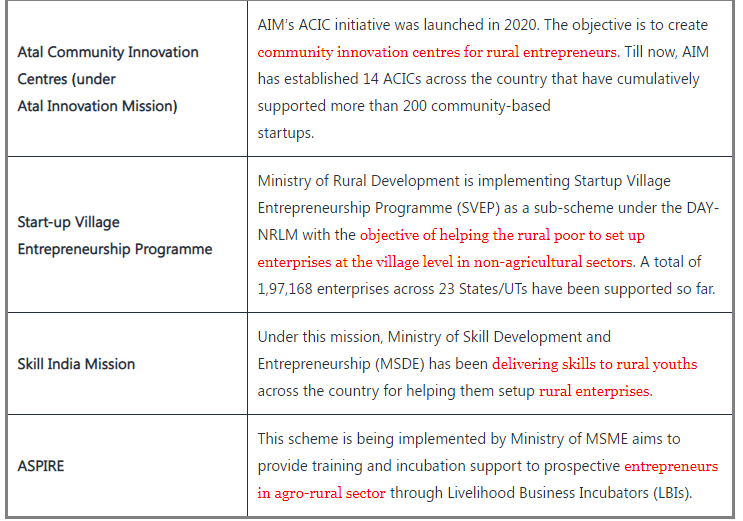
The way forward to support and empower rural startups in India involves strategic initiatives and collaborations:
- Policy Support: Governments should prioritize crafting policies tailored to address the unique challenges faced by rural startups, including infrastructure gaps, access to finance, and skill development. This involves incentivizing rural entrepreneurship and providing targeted support through policy frameworks.
- Community Engagement: Encourage and promote startups led by Self-Help Groups (SHGs) by facilitating community engagement and local participation. Strengthening SHG-led initiatives fosters community development and localized entrepreneurship.
- Government and NGO Collaboration: Foster collaboration between government agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), industry bodies, and other stakeholders to create comprehensive support ecosystems for rural startups. This collaboration can enhance access to resources, mentorship, and market linkages.
- Impact Measurement Mechanisms: Establish robust mechanisms for measuring the social and economic impact of rural startups. This involves tracking metrics such as employment generation, income enhancement, and community development to gauge the effectiveness of interventions and allocate resources efficiently.
- Focus on Sustainability: Emphasize sustainability over scalability for rural startups. Instead of solely pursuing unicorn status, prioritize building sustainable enterprises that generate meaningful employment and contribute to rural development aligned with the broader vision of inclusive and developed rural India (Vikshit Bharat).
[ad_2]
Source link


